Deb based distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, Kali uses the apt or apt-get commands for package management. Apt/apt-get commands use the official or 3rd party repositories in order to read package list, information, dependencies, update package information, download package and dependencies, etc. The apt update and apt upgrade commands mainly used to update package information and then upgrade packages according to updated information.
Update Package Information with apt update
The apt update or apt-get update command will update package information from the provided sources. These sources are generally network or internet provided repositories, CD/DVD or local files. But most of the cases the internet provided official or 3rd party repositories are used. We will also use the sudo command as these package manipulation requires root privileges which can be provided with the sudo command.
$ sudo apt update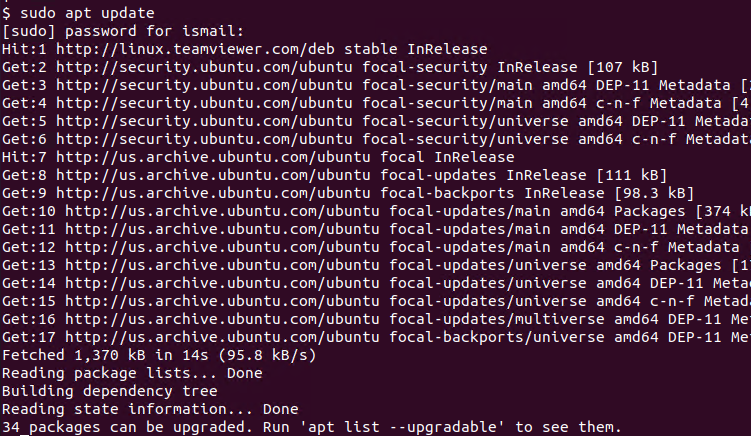
We can see that package information is provided via different repositories and according to these new information the updated package count is printed to the screen. For this example there are 34 packages which can be upgraded.
List Upgradeable Package with apt list –upgradable Command
Before upgrading packages, we may want to list the upgradable packages and related information. We will use the apt list --upgradable command like below.
$ apt list --upgradable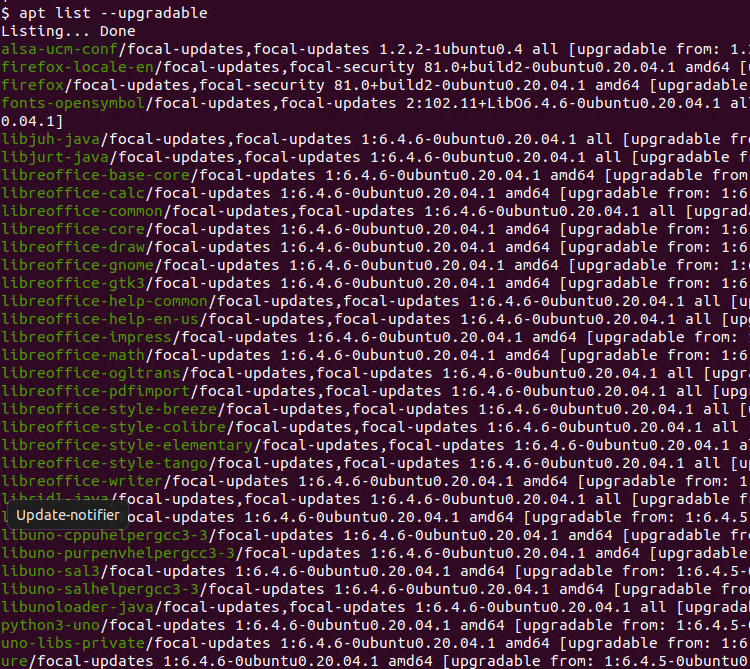
The output provides the package information version, older package version.
Upgrade Packages with apt upgrade or dist-upgrade
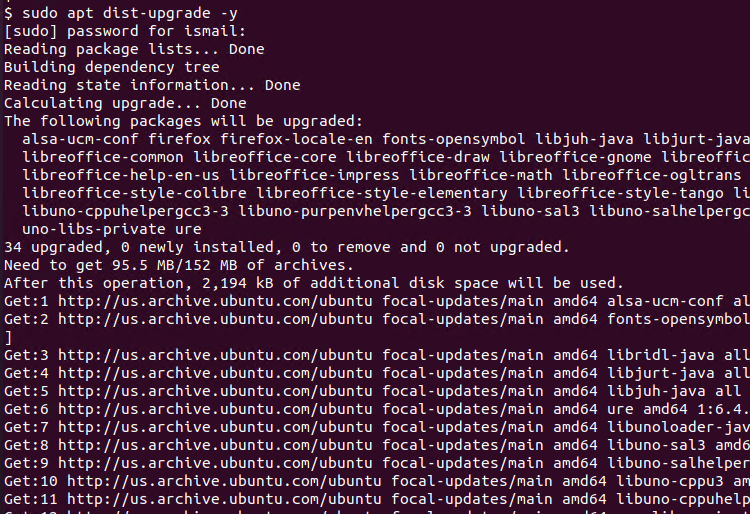
Now we can upgrade package with the apt upgrade or apt dist-upgrade . There is veryminor different between upgrade and dist-upgrade. When the upgrade is minor problems will be asked to the user where dist-upgrade will not ask and use default answers. I recommend you the dist-upgrade which is stable and straighforward.
$ sudo apt dist-upgrade -y