CPU or Central Processing Unit is the core part of the computers. CPU mainly processes data that is provided from different sources. CPU provides a lot of different features for different processing needs. These features and information about the CPU can be listed by using different commands in Linux.
/proc/cpuinfo File
One of the most fundamental source for the CPU information is the /proc/cpuinfo file. Most of the commands related to CPU info get information from this file. As a simple text file echo command can be used to print CPU information via the /proc/cpuinfo.
cat /proc/cpuinfoThe output is very detailed where following information is provided.
processor : 0 vendor_id : GenuineIntel cpu family : 6 model : 158 model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700HQ CPU @ 2.80GHz stepping : 9 microcode : 0xb4 cpu MHz : 2808.005 cache size : 6144 KB physical id : 0 siblings : 1 core id : 0 cpu cores : 1 apicid : 0 initial apicid : 0 fpu : yes fpu_exception : yes cpuid level : 22 wp : yes flags : fpu vme de pse ... flush_l1d arch_capabilities vmx flags : vnmi invvpid ept_x_only ... unrestricted_guest ple ept_mode_based_exec bugs : cpu_meltdown spectre_v1 spectre_v2 spec_store_bypass l1tf mds swapgs itlb_multihit srbds bogomips : 5616.01 clflush size : 64 cache_alignment : 64 address sizes : 45 bits physical, 48 bits virtual power management: processor : 1 vendor_id : GenuineIntel cpu family : 6 model : 158 model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700HQ CPU @ 2.80GHz stepping : 9 microcode : 0xb4 cpu MHz : 2808.005 cache size : 6144 KB physical id : 2 siblings : 1 core id : 0 cpu cores : 1 apicid : 2 initial apicid : 2 fpu : yes fpu_exception : yes cpuid level : 22 wp : yes flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr ... flush_l1d arch_capabilities vmx flags : vnmi invvpid ept_x_only ... unrestricted_guest ple ept_mode_based_exec bugs : cpu_meltdown spectre_v1 spectre_v2 spec_store_bypass l1tf mds swapgs itlb_multihit srbds bogomips : 5616.01 clflush size : 64 cache_alignment : 64 address sizes : 45 bits physical, 48 bits virtual power management:
lscpu Command
The lscpu command is another popular command which is used to list CPU information via the command-line interface. The cpuinfo command prints the CPU information in a more readable way. But the lscpu command provides less information than the /proc/cpuinfo file.
lscpuThe output is like below.
Architecture: x86_64 CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit Byte Order: Little Endian Address sizes: 45 bits physical, 48 bits virtual CPU(s): 2 On-line CPU(s) list: 0,1 Thread(s) per core: 1 Core(s) per socket: 1 Socket(s): 2 NUMA node(s): 1 Vendor ID: GenuineIntel CPU family: 6 Model: 158 Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700HQ CPU @ 2.80GHz Stepping: 9 CPU MHz: 2808.005 BogoMIPS: 5616.01 Virtualization: VT-x Hypervisor vendor: VMware Virtualization type: full L1d cache: 64 KiB L1i cache: 64 KiB L2 cache: 512 KiB L3 cache: 12 MiB NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0,1 Vulnerability Itlb multihit: KVM: Mitigation: VMX disabled Vulnerability L1tf: Mitigation; PTE Inversion; VMX flush not necessary, SMT disabled Vulnerability Mds: Mitigation; Clear CPU buffers; SMT Host state unknown Vulnerability Meltdown: Mitigation; PTI Vulnerability Spec store bypass: Mitigation; Speculative Store ... and seccomp Vulnerability Spectre v1: Mitigation; ... and __user pointer sanitization Vulnerability Spectre v2: Mitigation; Full generic retpoline, ... sabled, RSB filling Vulnerability Srbds: Unknown: Dependent on hypervisor status Vulnerability Tsx async abort: Not affected Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr ... xsaves arat md_clear flush_l1 arch_capabilities
- Architecture lists if the CPU is 32 bit or 64 bit or an ARM processor.
- CPU ops-mode prints if the CPU runs 32-bit or 64-bit applications or both of them.
- Model Name provides the manufacturer and model name of the CPU.
cpuid Command
The cpuid command provides similar information where the CPU information is extracted by using the CPUID instruction. It provides information like vendor ID, CPU Family, etc. Most of the Linux distributions do not come preinstalled with the cpuid command. The cpuid can be installed like below.
Install cpuid For Ubuntu, Debian, Mint:
sudo apt install cpuidInstall cpuid For CentOS, RHEL, Fedora:
sudo yum install cpuidAfter installing we will run the cpuid command like below. The cpuid command lists every core of the processor separately.
cpuidThe output is like below.
CPU 0:
vendor_id = "GenuineIntel"
version information (1/eax):
processor type = primary processor (0)
family = 0x6 (6)
model = 0xe (14)
stepping id = 0x9 (9)
extended family = 0x0 (0)
extended model = 0x9 (9)
(family synth) = 0x6 (6)
(model synth) = 0x9e (158)
(simple synth) = Intel Core (unknown type) (Kaby Lake / Coffee Lake) 14nm
miscellaneous (1/ebx):
process local APIC physical ID = 0x0 (0)
maximum IDs for CPUs in pkg = 0x1 (1)
CLFLUSH line size = 0x8 (8)
brand index = 0x0 (0)
brand id = 0x00 (0): unknown
feature information (1/edx):
x87 FPU on chip = true
VME: virtual-8086 mode enhancement = true
DE: debugging extensions = true
PSE: page size extensions = true
TSC: time stamp counter = true
RDMSR and WRMSR support = true
PAE: physical address extensions = true
MCE: machine check exception = true
...
dmidecode Command
dmidecode is a very useful command which simply retrieves and displays all hardwares and related information. The dmidecode do not onlydisplay information about CPU also provides information about Mainboard, RAM, Graphic Card, HDD, SSD etc. In order to display only CPU related information the –type processor parameter should be provided. As a complex command the dmidecode requires root privileges to access detailed information. The root access can be provided with the sudo command.
sudo dmidecode --type processorThe output is like below. The following information is about first CPU code which is number as Core0 and all other cores information is printed like below.
dmidecode 3.2
Getting SMBIOS data from sysfs.
SMBIOS 2.7 present.
Handle 0x0004, DMI type 4, 42 bytes
Processor Information
Socket Designation: CPU #000
Type: Central Processor
Family: Unknown
Manufacturer: GenuineIntel
ID: E9 06 09 00 FF FB 8B 0F
Version: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700HQ CPU @ 2.80GHz
Voltage: 3.3 V
External Clock: Unknown
Max Speed: 30000 MHz
Current Speed: 2800 MHz
Status: Populated, Enabled
Upgrade: ZIF Socket
L1 Cache Handle: 0x0094
L2 Cache Handle: 0x0114
L3 Cache Handle: Not Provided
Serial Number: Not Specified
Asset Tag: Not Specified
Part Number: Not Specified
Core Count: 1
Core Enabled: 1
Characteristics:
64-bit capable
Execute Protection
Enhanced Virtualization
...
inxi Command
The inxi is very simple tool which provides very basic information about the CPU. the inxi is not installed by default for popular Linux distributions and can be installed like below.
Debian, Ubuntu, Mint, Kali:
sudo apt install inxiCentOS, RHEL, Fedora:
sudo yum install inxiThe inxi tool provides information about all hardware but we can use the -C option in order to print information about CPU or processor.
inxi -CThe inxi output is formatted and colored like below.
CPU: Info: 2x Single Core model: Intel Core i7-7700HQ bits: 64 type: SMP L2 cache: 12.0 MiB
Speed: 2808 MHz min/max: N/A Core speeds (MHz): 1: 2808 2: 2808
lshw Command
The lshw is a small tool which is used to extract detailed information about the hardware. The CPU or processor information can be listed by using the -C CPU option like below. The lshw command reuqires the root privileges which can be provided with the sudo command.
sudo lshw -C CPU
The output is like below.
*-cpu:0
description: CPU
product: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-10510U CPU @ 1.80GHz
vendor: Intel Corp.
physical id: 1
bus info: cpu@0
version: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-10510U CPU @ 1.80GHz
slot: CPU #000
size: 2300MHz
capacity: 4230MHz
width: 64 bits
capabilities: lm fpu fpu_exce ... md_clear flush_l1d arch_capabilities
configuration: cores=4 enabledcores=4
hardinfo Tool (GUI)
The hardinfo tool is a tool used to provide hardware information about the system. The hardinfo is a graphical tool which is different from other tools we have listed. The hardinfo also provides benchmark for the current system. The hardinfo is not installed by default in most of the Linux distributions.
Debian, Mint, Kali, Ubuntu:
sudo apt install hardinfo
CentOS, RHEL, Fedora:
sudo yum install hardinfo
The hardinfo tool can be opened from the start menu of the desktop environment or by running the hardinfo command from the bash shell.
hardinfo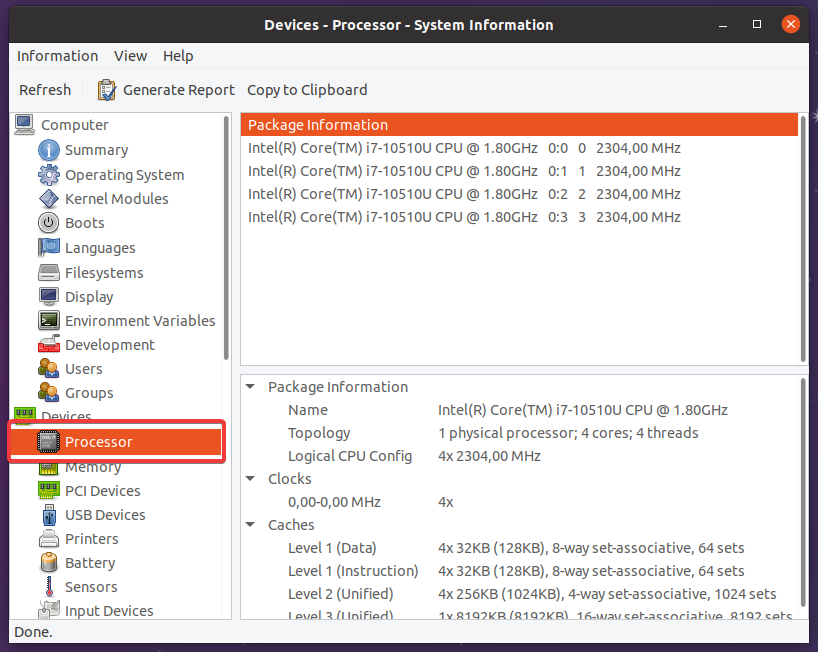
hwinfo command
The hwinfo command provides detailed information about the current hardware in the Linux system. The hwinfo is not installed by default and can be installed like below.
Debian, Mint, Ubuntu, Kali:
sudo apt install hwinfoRHEL, CentOS, Fedora:
sudo yum install hwinfoThe get only CPU related information the –cpu option should be provided like below.
hwinfo --cpuThe output is like below.
01: None 00.0: 10103 CPU [Created at cpu.465] Unique ID: rdCR.j8NaKXDZtZ6 Hardware Class: cpu Arch: X86-64 Vendor: "GenuineIntel" Model: 6.142.12 "Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-10510U CPU @ 1.80GHz" Features: fpu,vme,de,pse ... h_l1d,arch_capabilities Clock: 2304 MHz BogoMips: 4608.00 Cache: 8192 kb Units/Processor: 4 Config Status: cfg=new, avail=yes, need=no, active=unknown
