Directories or folders can contain multiple files and directories. These multiple files and directories use some disk space and have a size. But when we list the files and directories we see that the directory size is listed as 4096 bytes or 4KB. This is the directory standard size which does not contain the files and directories sizes. So how can get the size of the directory or folder with its contents?
Get Size of Directory with du Command
The du command is used to get disk usage for files and directories. The du name comes from the term “disk usage“. The du command provides a lot of features for different cases. By default, the du command lists all files and directories sizes in a recursive manner. This creates a lot of output because of the recursive behavior.
$ du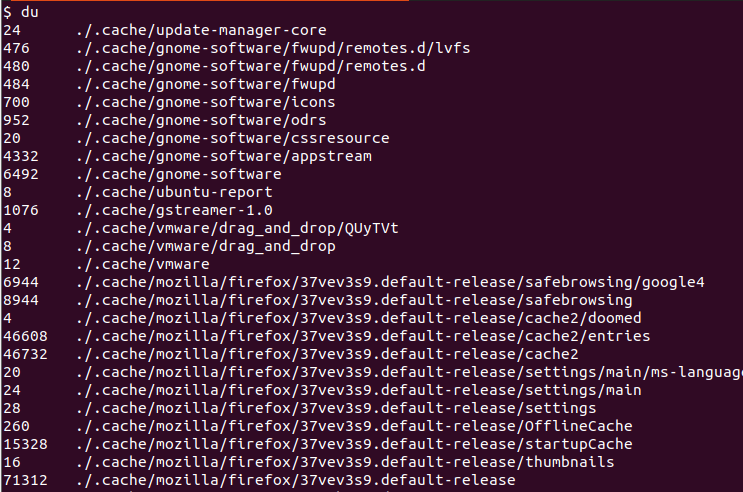
The output displays the directories as bytes for example the update-manage-core directory is 24 bytes.
Get Current Working Directory Size
The current working directory size can be displayed with the du command adding -s and -h options. By default, the du command lists all files and directories sizes recursively. But the -s option is used to show the total or summary size of the current working directory.
$ du -shThe output is like below where the point is used to specify the current working directory. In this example, the current working directory size is 185 MB.
185M .
Alternatively, all files and directories sizes of the current working directory can be listed by using the glob operator like below.
$ du -sh *The output is like below.
4,0K data1 4,0K data2 4,0K data3 4,0K data4 4,0K data5 4,0K Desktop 4,0K Documents 4,0K Downloads 0 file1 0 file2 0 file3 0 file4 4,0K Music 0 myfile 4,0K myfolder 0 mylink 4,0K names.txt 0 newfile 11M nmap-7.91.tar.bz2 452K Pictures 4,0K Public 4,0K read_line_by_line.sh 4,0K sample.txt 20K Templates 4,0K test 0 text.txt 4,0K thinclient_drives 4,0K userinput.py 4,0K Videos 8,0K year
Get Specified Directory Size
A specific directory or path can be specified in order to get its size. Just provide the path to the du command. In the following example, we will get the size of the home directory of the user ismail .
$ du -csh /home/ismailThe output is like below.
185M /home/ismail 185M total
Get Specific Level Directory Size
By default, the du command works as recursive and lists and adds all sub files and folders size for the specified directory. But the –max-depth option can be used to specify the level of the directories we want to list. For example –max-depth=1 is used to list first-level sizes for the directories.
$ du -h --max-depth=1 /home/ismailThe output is like below.
91M /home/ismail/.cache 452K /home/ismail/Pictures 4,0K /home/ismail/data2 31M /home/ismail/.mozilla 4,0K /home/ismail/data4 4,0K /home/ismail/Desktop 4,0K /home/ismail/Videos 4,0K /home/ismail/Downloads 7,1M /home/ismail/.oh-my-zsh 4,0K /home/ismail/data5 4,0K /home/ismail/thinclient_drives 4,0K /home/ismail/Documents 4,0K /home/ismail/data1 348K /home/ismail/.config 20K /home/ismail/.ssh 4,0K /home/ismail/Music 46M /home/ismail/.local 4,0K /home/ismail/data3 20K /home/ismail/Templates 16K /home/ismail/.gnupg 8,0K /home/ismail/year 4,0K /home/ismail/Public 4,0K /home/ismail/myfolder 185M /home/ismail
Sort Directories According To Their Sizes
Another popular use case for the directory sizes is sorting directories according to their sizes. By default directories and sizes are listed according to their name alphabetically. but we can use the sort command in order to sort directories according to their sizes.
$ du -ch /home/ismail/* | sort -rhThe output is like below.
11M total 11M /home/ismail/nmap-7.91.tar.bz2 452K /home/ismail/Pictures 20K /home/ismail/Templates 8,0K /home/ismail/year 4,0K /home/ismail/year/2020 4,0K /home/ismail/Videos 4,0K /home/ismail/userinput.py 4,0K /home/ismail/thinclient_drives 4,0K /home/ismail/test 4,0K /home/ismail/sample.txt 4,0K /home/ismail/read_line_by_line.sh 4,0K /home/ismail/Public 4,0K /home/ismail/names.txt 4,0K /home/ismail/myfolder 4,0K /home/ismail/Music 4,0K /home/ismail/Downloads 4,0K /home/ismail/Documents 4,0K /home/ismail/Desktop 4,0K /home/ismail/data5 4,0K /home/ismail/data4 4,0K /home/ismail/data3 4,0K /home/ismail/data2 4,0K /home/ismail/data1 0 /home/ismail/text.txt 0 /home/ismail/newfile 0 /home/ismail/mylink 0 /home/ismail/myfile 0 /home/ismail/file4 0 /home/ismail/file3 0 /home/ismail/file2 0 /home/ismail/file1
du: cannot read directory ‘…’: Permission denied Error
While working with the du command we may get the “du: cannot read directory ‘…’: Permission denied” error. This error cause is the current user permissions are not enough to read the provided directory. These directories are generally owned by the root or alternatively root or sudo users can read these directories. So simply providing the sudo command solves this error.
du: cannot read directory '/var/lib/sss/keytabs': Permission denied du: cannot read directory '/var/lib/sss/secrets': Permission denied du: cannot read directory '/var/lib/mysql-keyring': Permission denied du: cannot read directory '/var/log/private': Permission denied du: cannot read directory '/var/log/gdm3': Permission denied du: cannot read directory '/var/log/sssd': Permission denied du: cannot read directory '/var/log/speech-dispatcher': Permission denied du: cannot read directory '/var/spool/cron/crontabs': Permission denied du: cannot read directory '/var/spool/rsyslog': Permission denied du: cannot read directory '/var/spool/cups': Permission denied 3,4G total 1,7G /var/log 1,4G /var/lib 345M /var/cache 5,2M /var/backups 1,4M /var/snap 48K /var/spool
Solve this error with the sudo command like below.
sudo du -csh /var/* | sort -rhGet Size of Directory with ncdu Command
Most of the Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Mint, RHEL, etc provides the ncdu command. It can be installed like below.
Install ncdu for Debian, Mint, Ubuntu, Kali:
$ sudo apt install ncduInstall ncdu for RHEL, CentOS, Fedora:
$ sudo dnf install ncduJust run the ncdu command like below which lists the current working directory content and their sizes.
$ ncdu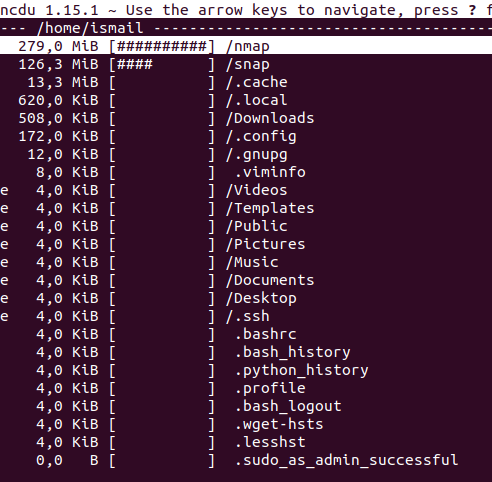
Get Size of Directory with File Manager (GUI)
File Managers are GUI tools to manage files and directories. The file manager can be also used to get a directory size. First, open the file manager and right-click on the directory you want to get the size. Select the Properties below.
The following directory properties screen provides information about the directory. The size of the directory is also listed in the Contents line where the contents count and the total size of the directory are listed.
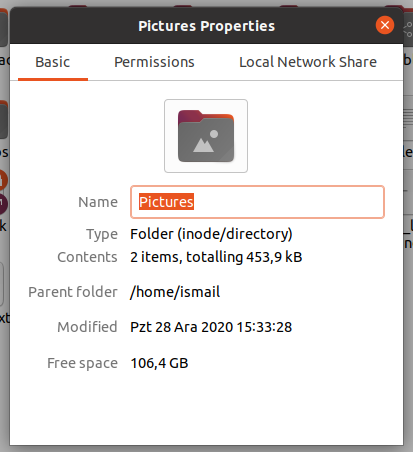
We can see that a lot of information about the Pictures directory is provided. The Size of the directory is 453,9 kB or kilobyte.
