Linux is a file-based operating system where everything is a file. As a file-based operating system, there are a lot of tools and commands related to the files. The lsof command is used to find a list of opened files by a process. The name lsof comes from “LiSt of Opened Files”. The lsof command is very useful because already opened and not closed files can not be moved or deleted or related file systems can not be unmounted etc.
lsof Command Syntax
The lsof command has the following syntax which is the same with the other Linux commands.
lsof OPTIONS- OPTIONS may be a process ID or protocol name etc. OPTIONS is optional.
List All Opened Files
Without providing any parameter is option to the lsof command lists all opened files and related process. This will create a long list as a single process can opened multiple files in general.
lsof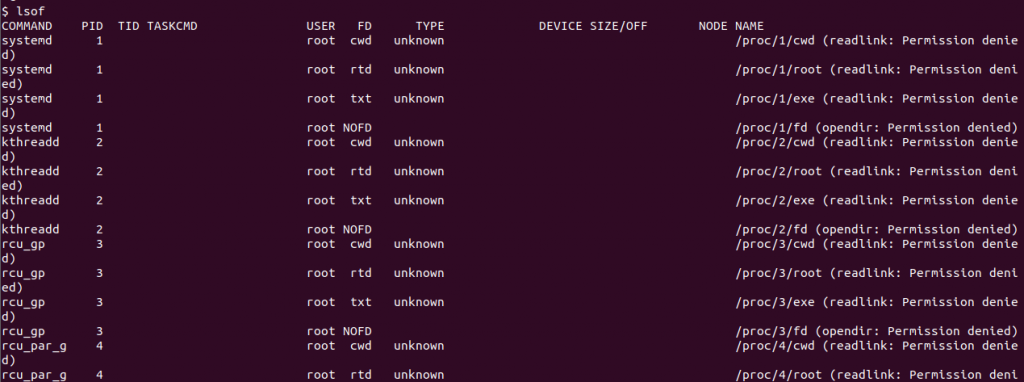
Here some columns like COMMAND, PID etc. listed for the lsof command output.
- COMMAND is the command or executable name which opened the file.
- PID is the process ID or the command or executable.
- TID is the Task ID.
- USER is the process owner user name
- FD is File Descriptor which can be cwd, rtd, txt and mem. Also, there are some access modes like r for reading, w for write access, and u for reading and write access.
- TYPE specifies the file type which can be DIR (regular directory), REG (regular file), CHR (character device), and FIFO (first in first out).
List All Opened Files For A Specific User
By default the lsof command lists all processes and opened files for all users. But we can limit or filter the opened files and processes for a specific user. We will use the -u option and provide the username. In the following example we will list all opened files and processes for the user ismail.
lsof -u ismailFind Process For The Open/Listening Port
The lsof command also used to find the process which is opened is listening for a specific network (TCP/UDP) port. For example, ssh listen for the port number TCP 22. We will specify the protocol type which can be TCP or UDP and the port numbers like 22 and the -i parameter like below. We will also provide the sudo command as the port and socket related operations require root privilege.
sudo lsof -i TCP:22The output like below.
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME sshd 916 root 3u IPv4 39812 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) sshd 916 root 4u IPv6 39814 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN)
List Only IPv4 Ports
IPv4 and IPv6 are two different IP protocol versions where IPV4 is currently more popular but IPv6 is the next generation. We can only list the IPv4 protocol connections and listening ports like below.
sudo lsof -i 4The list is like below.
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME systemd-r 712 systemd-resolve 12u IPv4 35310 0t0 UDP localhost:domain systemd-r 712 systemd-resolve 13u IPv4 35311 0t0 TCP localhost:domain (LISTEN) avahi-dae 755 avahi 12u IPv4 39552 0t0 UDP *:mdns avahi-dae 755 avahi 14u IPv4 39554 0t0 UDP *:50799 NetworkMa 760 root 22u IPv4 159669 0t0 UDP ubuntu:bootpc->192.168.146.254:bootps sshd 916 root 3u IPv4 39812 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) mysqld 1056 mysql 32u IPv4 49638 0t0 TCP localhost:33060 (LISTEN) mysqld 1056 mysql 34u IPv4 48316 0t0 TCP localhost:mysql (LISTEN) cupsd 5625 root 7u IPv4 134297 0t0 TCP localhost:ipp (LISTEN) cups-brow 5628 root 7u IPv4 134314 0t0 UDP *:631
List Only IPv6 Ports
Also only IPv6 ports can be listed with the -i 6 like below.
sudo lsof -i 6The opened or listening IPv6 ports and related processes are like below.
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME avahi-dae 755 avahi 13u IPv6 39553 0t0 UDP *:mdns avahi-dae 755 avahi 15u IPv6 39555 0t0 UDP *:50825 sshd 916 root 4u IPv6 39814 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) xrdp-sesm 917 root 7u IPv6 40965 0t0 TCP ip6-localhost:3350 (LISTEN) xrdp 959 xrdp 11u IPv6 44724 0t0 TCP *:ms-wbt-server (LISTEN) apache2 971 root 4u IPv6 42125 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN) apache2 5619 www-data 4u IPv6 42125 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN) apache2 5620 www-data 4u IPv6 42125 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN) apache2 5621 www-data 4u IPv6 42125 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN) apache2 5622 www-data 4u IPv6 42125 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN) apache2 5623 www-data 4u IPv6 42125 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN) cupsd 5625 root 6u IPv6 134296 0t0 TCP ip6-localhost:ipp (LISTEN)
List Only TCP Ports
Only TCP ports can be listed by using the “-i TCP” like below.
sudo lsof -i TCPList Only Specified Range TCP Port Numbers
Opened or listening ports can be listed according to the port numbers. The port range can be specified by providing the start number and end number. In the following example we will only list processes using TCP port numbers 1 and 2048.
sudo lsof -i TCP:1-2048List All Network Connections
All network conenctions can be listed with the -i option. This will list all opened or listening network connections for IPv4, IPv6, TCP and UDP.
sudo lsof -iList Opened Files with Process ID (PID)
We can use the process ID or PID in order to filter processes. The -p option and process ID is used to file opened or listening port numbers of the processes. In the
lsof -p 8731The output is like below.
bash 8731 ismail cwd DIR 8,3 4096 5643833 /home/ismail bash 8731 ismail rtd DIR 8,3 4096 2 / bash 8731 ismail txt REG 8,3 1183448 4456540 /usr/bin/bash bash 8731 ismail mem REG 8,3 55904 4463960 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnss_files-2.32.so bash 8731 ismail mem REG 8,3 17360800 4462545 /usr/lib/locale/locale-archive bash 8731 ismail mem REG 8,3 1995896 4463186 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.32.so bash 8731 ismail mem REG 8,3 18816 4463329 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libdl-2.32.so bash 8731 ismail mem REG 8,3 192032 4464308 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libtinfo.so.6.2 bash 8731 ismail mem REG 8,3 27002 5115982 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/gconv/gconv-modules.cache bash 8731 ismail mem REG 8,3 195584 4462972 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-2.32.so bash 8731 ismail 0u CHR 136,1 0t0 4 /dev/pts/1 bash 8731 ismail 1u CHR 136,1 0t0 4 /dev/pts/1 bash 8731 ismail 2u CHR 136,1 0t0 4 /dev/pts/1 bash 8731 ismail 255u CHR 136,1 0t0 4 /dev/pts/1
