Linux distributions provide different tools to manage services. Recently the systemctl command which is provided by the systemd tool is the most popular and widely used tool. Services are created and executed in order to provide different resources to local and remote users. In this tutorial we will learn how to use the systemctl command in order to list all, running, stopped services in a Linux system. systemctl command is provided by most of the Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Mint, Kali, Debian, Fedora, CentOS, RHEL, SUSE, etc. and can be used without a problem.
List All Services
We can run the systemctl command without any parameter which will display all system units in order word services. This list provides information like Unit/Service name, Active, is currently running, description of the service.
$ systemctl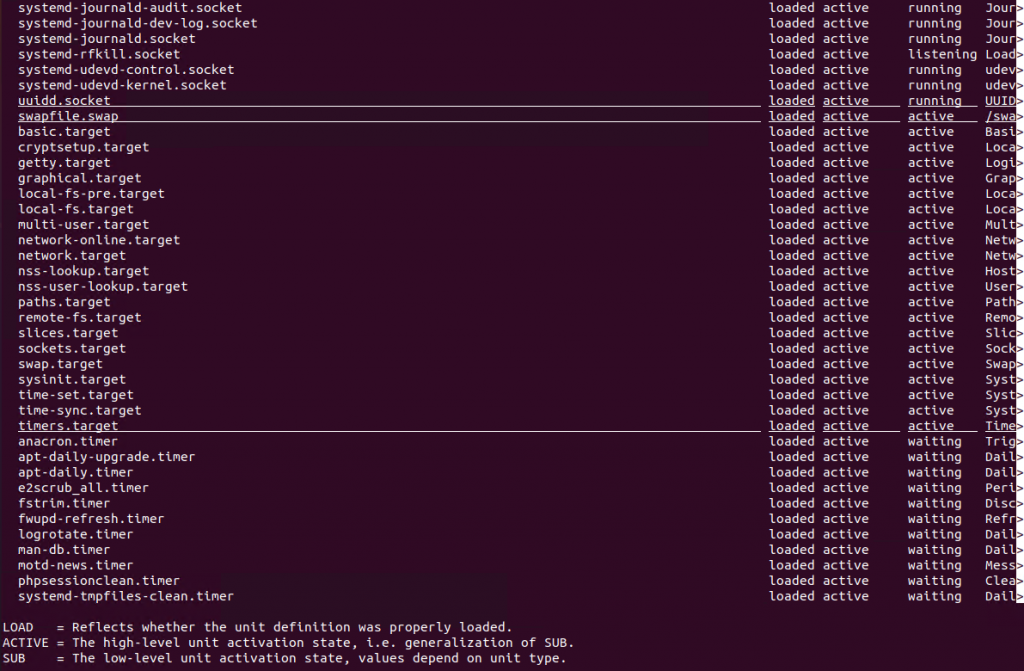
Alternatively we can provide parameters to list all loaded services with the list-units --type=service parameter like below.
$ systemctl list-units --type=servicesOr alternatively.
$ systemctl --type=serviceList All Running Services
Services can be started, restarted or stopped at any time. A service which is started called as running service can be listed with the --type=service --state=running parameters like below.
$ systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running alternatively
$ systemctl --type=service --state=running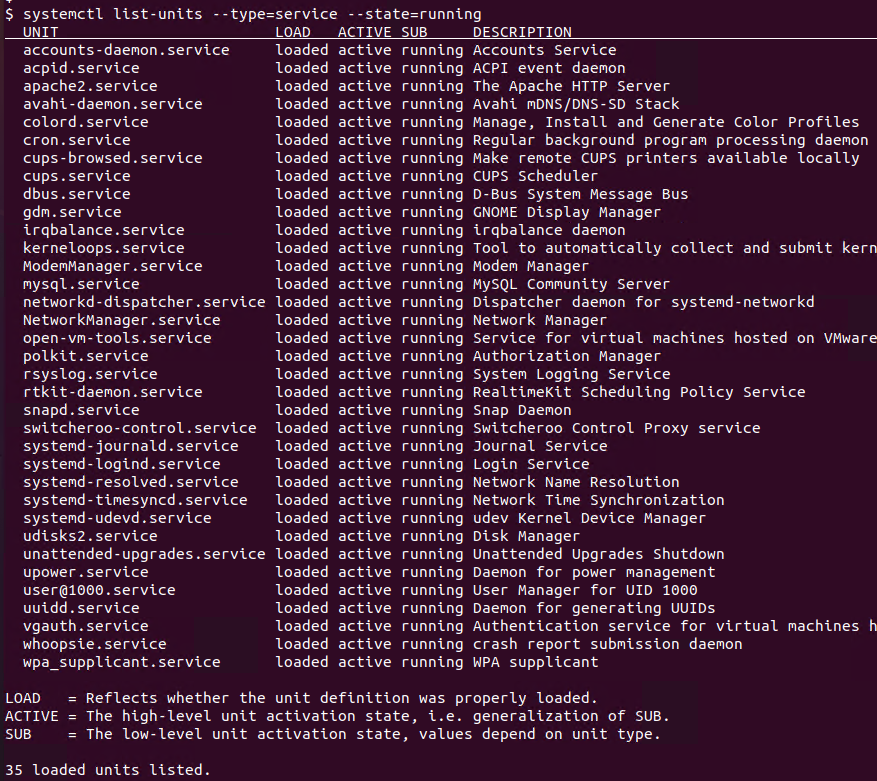
There is also an alternative way where the systemctl command output will be grepped for the term running like below. The systemctl command will be piped into the grep command.
$ systemctl | grep runningList All Active/Enabled Services
Some services are set to start during boot of the system. These services will automacally start after system start or restart. The services starting during boot are called as Active Service or Enabled Service . The active or enabled services can be listed by using the --stat=active parameter like below.
$ systemctl list-units --type=service --state=activeor alternatively;
$ systemctl --type=service --state=active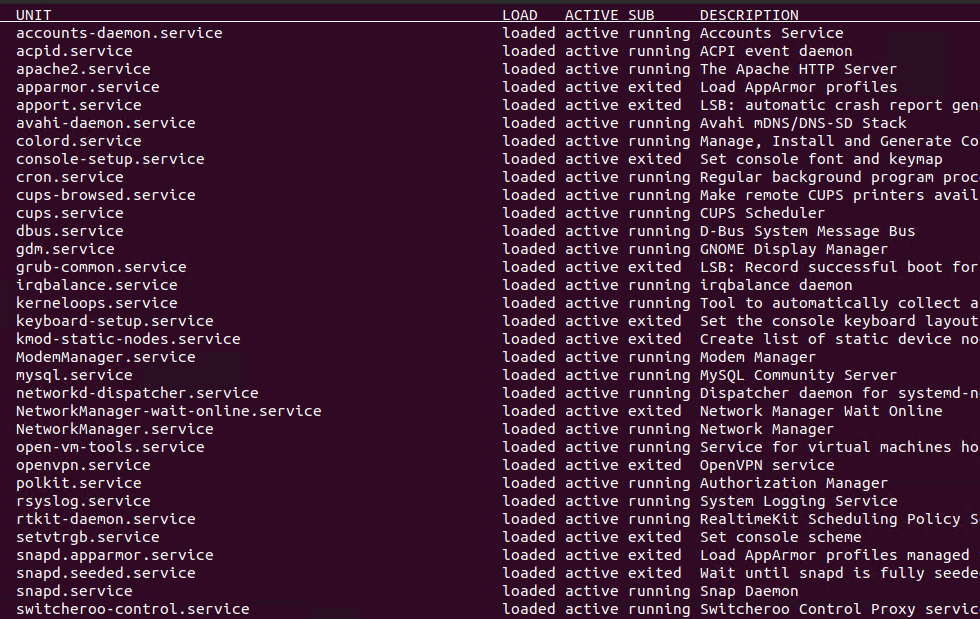
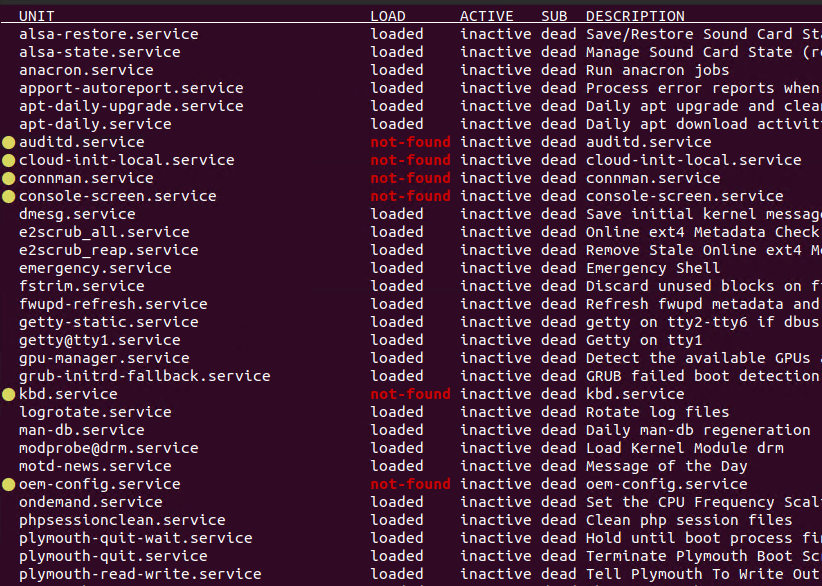
List All Inactive/Disabled Services
We can also list inactive or disable services which will not start during boot automatically. We will use the --type=service --status=inactive parameter like below.
$ systemctl list-units --type=service --state=inactive