Zip is a compression algorithm and format used to package given files and folders to use less disk space. The zip files have generally the *.zip extension and different tools that can be used to create, add, remove or extract zip files. But the most prolific tool and command is the zip command in Linux operating systems.
zip Command Syntax
The zip command syntax is like below.
zip OPTION ZIP_FILE FILES_FOLDERS- OPTION is used to provide different options to the zip file.
- ZIP_FILE is the file name of the zip file.
- FILES_FOLDERS can be single or more files and folders which will be zipped into the ZIP_FILE.
Install zip Command
In some cases the zip command is not installed by default. We may need to install zip command explicitly.
Install zip Command In Ubuntu, Debian, Mint, Kali:
$ sudo apt install zipInstall zip Command In Fedora, RHEL, CentOS:
$ sudo dnf install zipzip Command Help
The zip command is very old and actively developed command and provides detailed help information about its usage. The simplest and less informative way to get help is running the zip command without any option or parameter.
$ zip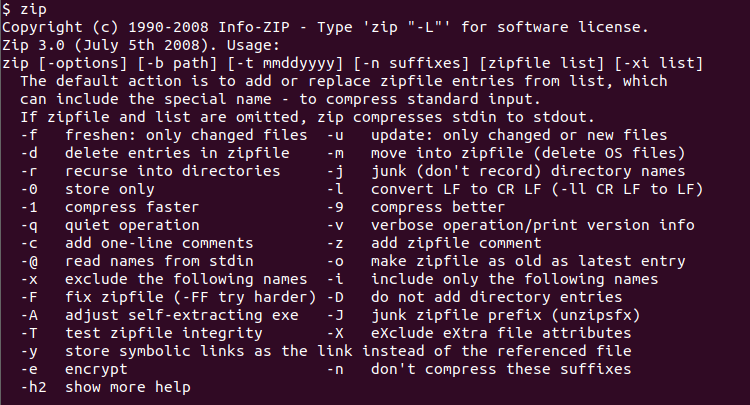
More detailed help can be listed with the -h2 option to the zip command like below.
$ zip -h2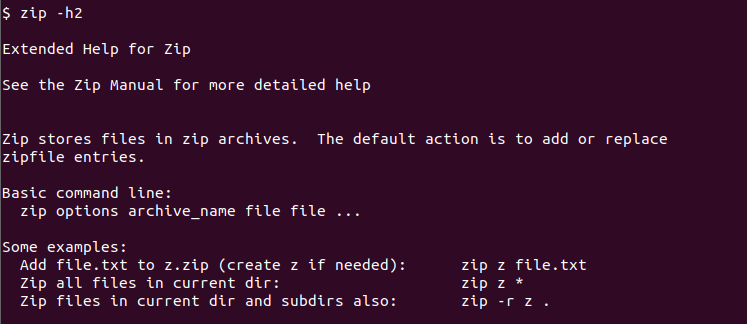
Zip A File
Let’s start with a simple example where we zip a single file named cities.txt . The zip file is named as cities.zip like below. There is no need to add an extra parameter to zip it.
$ zip cities.zip cities.txtadding: cities.txt (deflated 15%)
Zip Multiple Files
We can also zip multipe files in a single step. We just provide the files we want to zip. In the following example we zip files named cities.txt , MyFile.csv and myshell.txt into zip file named my.zip .
$ zip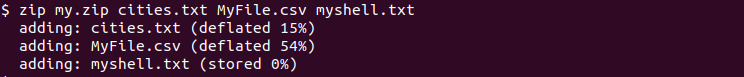
Add New File To Zipped File
New files can be added to the existing zip file. Just provide the zip file name and the file name we want to add. In the following example we add the file numbers.txt into the zip file named my.zip .
$ zip my.zip numbers.txtDelete/Remove A File From Zip File
A single file can be removed from the zipped file. The -d option is used to remove the specified file. In the following example, we remove the file named myshell.txt from the zipped file named my.zip .
$ zip -d my.zip myshell.txtdeleting: myshell.txt
If the specified file is deleted or removed from the zip file the previous deleting: line is printed with the deleted file name.
Zip Files and Folders Recursively
Normally when we specify a folder to zip only the folder is zipped and its contents are not zipped. In order to zip a folder or directory with its files and child folders and directories it should be zipped recursively. The -r option is used to zip files and folders recursively.
$ zip -r Downloads.zip Downloads/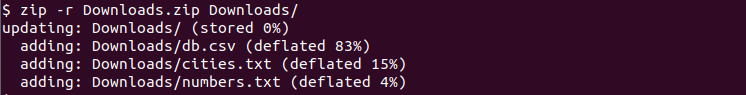
Print Details About Zip Operation, Files and Folders
The zip command and operation executes different steps. More detailed information about the zip operation can be printed as verbose mode. The -v option is used to print detailed verbosely which can be also called as debugging the zip.
$ zip -r -v Downloads.zip Downloads/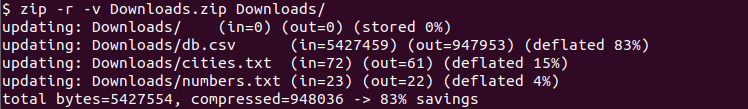
Suppress Output Do Not Print Information
We can prevent the zip command printing information about the zip process and related files and folders names. We should suppress the output with the -q option like below.
$ zip -r -q Downloads.zip Downloads/