ISO is a popular file format that is generally used to store optical media data like CDs, DVDs, etc. ISO files contain the image of a specific CD or DVD. Generally, operating systems, software, software bundles are stored inside ISO files. ISO is a file format and file system which is also defined as ISO 9660. ISO 9660 standard created in order to make every CD and DVD content compatible. The UDF is the next version of the ISO 9660 standard. UDF is backward compatible with the ISO 9660.
Mount ISO File with mount Command
The mount command is used to mount different disks and partitions with different file systems. As an ISO file is a file system defined as ISP 9660 or UDF we can use the mount command in order to mount ISO files. To mount the ISO file a mount point is required where the contents of the ISO represented. In the following example, the ISO file named ubuntu.iso mounted into cdrom directory located in the current user home directory. We provide the -o loop option and do not provide the sudo command. Following ISO mount operation does not require root privileges because the current user has access rights for his/her home directory.
mount -o loop /home/ismail/ubuntu.iso /home/ismail/cdromGenerally physical CD-ROM and ISO files are mounted under the /mnt directory. The /mnt directory requires root privielges to mount or create directory. First we will create a directory named /mnt/iso to mount ISO file.
sudo /mnt/isoNow we can mount the ISO file but again we require the root privileges. We provide the sudo command.
sudo -o loop /home/ismail/ubuntu.iso /mnt/isoBy default the ISO file file system type is automatically detected by the mount command. But in some cases it may not work. The file system type of the ISO file can be specified explicitly. The -t iso9660 can be specified as the file system like below.
sudo -o loop -t iso9660 /home/ismail/ubuntu.iso /mnt/isoList ISO File Contents
After mounting ISO file we can list the contents of the ISO file. We use the ls command to list mount directory contents. In the following example the ISO file is mounted under /mnt/iso .
ls /mnt/isoUnmount ISO File with umount Command
The mounted ISO file can be unmounted by using the umount command. Just provide the mount directory of the ISO file to the umount command. In the following example, we unmount the /mnt/iso .
sudo umount /mnt/isoIf the directory is its contents allready in use it can not be unmounted and return error about this.
Mount ISO File In GNOME Desktop
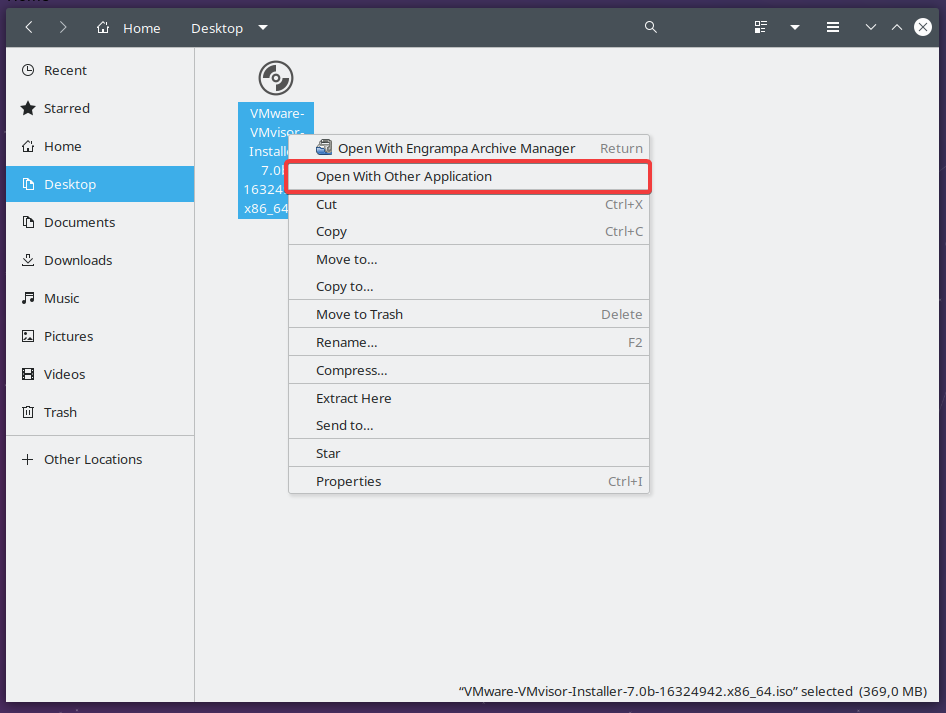
GNOME is a popular desktop environment used in Linux. It provides the tool named Disk Image Mounter which can be used to mount ISO files. First right-click to the ISO file like below. Select the “Open With Other Application” if the “Open With Disk Image Mounter” not listed.
In the following Select Application screen select the Disk Image Mounter. As the last step click to the Select button. This mounts the ISO file automatically.
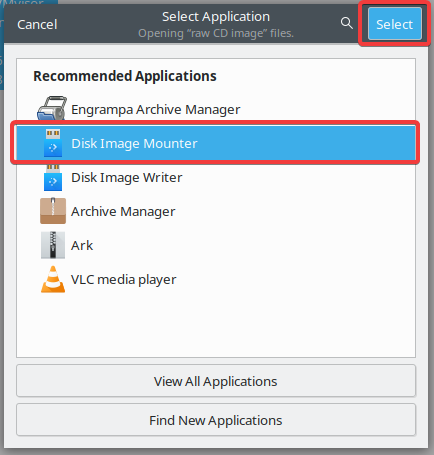
After the ISO file mounted it listed in the File Manager menu side bar like below.