Linux provides directories in order to store other directories and files. One of the most popular daily tasks is copying directories and their contents. The cp command can be used to copy directories in Linux. But there are different ways to copy directories like recursive, preventing overwrite, interactive, etc.
Copy Directory with cp Command
The cp command is used to copy files and folders. The name cp comes from the copy word. The cp command has the following simple syntax.
cp OPTIONS SOURCE DESTINATION- OPTIONS is used to specify different options for the cp command.
- SOURCE is the source directory or directory those will be copied to DESTINATION.
- DESTINATION is the destination directory.
In the following example, we copy the directory named db as db_Backup . Keep in mind that the cp command without any option only copies provided directories but not their content.
$ cp db db_BackupCopy Directory and Its Content Recursively
In order to copy the specified directory and all of its contents, the recursive option should be used. The -R option is used to copy directories recursively. By copying, recursively specified source directory and all child directories and files are copied to the destination. In the following example, we copy the directory /home/ismail to /mnt/backup with all of its child contents.
$ cp -R /home/ismail /mnt/backupCopy Directory Content Recursively
Alternatively, we can copy only the content of the specified directory and not the directory. This will also copy all child contents like directories and files for the specified directory. In the following example, we copy child files and directories of the /etc but not copy the /etc directory.
$ cp -R /etc/* /mnt/backupCopy Multiple Directories
The cp command can be used to copy multiple directories into the specified directory. The multiple source directories are provided before the destination directory. In the following example, we will copy /home/ismail/ , /etc/ and /home/ahmet into the /mnt/backup .
$ cp -R /home/ismail /etc /home/ahmet /mnt/backupCopy Directory Preventing Overwriting Files
If the destination directory contains the source files or directories it may overwrite these destination files and directories. The -n or -no-clobber option can be used to prevent overwriting for the destination.
$ cp -R -n /etc/* /mntCopy Directory Interactively
Another useful option during copying a directory is interactive copy where if the source file or directory exists in destination the confirmation is requested in an interactive way. The -i option is used for interactive copy.
$ cp -R -i /home/ismail /mnt/backupDisplay Verbose Output and List Copied Directories
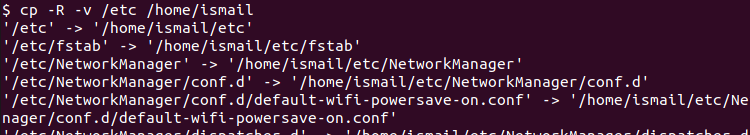
During directory copy, a lot of files or directories can be copied. These copied files and directories are not listed or displayed by default. The verbose option -v can be used to display all copied files and directories during the copy.
$ cp -R -v /etc /home/ismail