The Linux operating system provides the rmdir command in order to remove directories. But there is an important point where the rmdir command can only delete an empty directory. If a directory has some files it can not be deleted with the rmdir command. The rmdir name comes from Remove Directory .
Remove Empty Directory
The rmdir command can be used to delete an empty directory. The directory path or name is provided as a parameter to the rmdir command. In the following example, we remove the directory named data.
$ rmdir dataWe can also delete a directory using its full path with the rmdir command. This is a better way to delete a directory because there is very little room for mistakes in the directory name and path.
$ rmdir /home/ismail/data/Remove Non-Empty Directory
Well, we have already said that the rmdir command can only delete an empty directory but if we need to delete a non-empty directory what should we do? There is a rm command which can be used to delete non-empty directly. The directory contains some files and directories.
$ rm -rf /home/ismail/data/Remove Multi-Level Path/Directory
The rmdir command can be used to remove multi-level directories or paths. But all of the directories should be empty. The -p option is used to delete the multi-level directory. But all directories do not have any files.
$ rmdir -p ./data/backup/testRemove Directory Verbosely
By default, while deleting directories with the rmdir command no information about the operation is displayed. We can display information with the -v verbose option like below.
$ rmdir -v datarmdir Version
The rmdir command version information can be displayed by using the --version option.
$ rmdir --version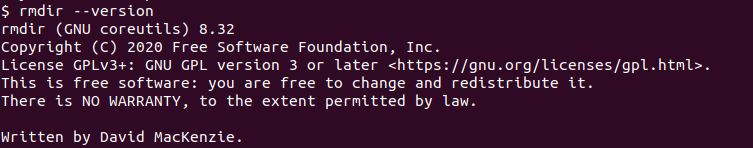
rmdir Help
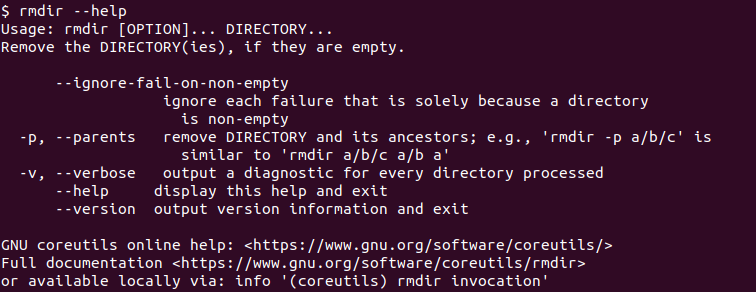
We can also print the help information about the rmdir command by using the --help option.
$ rmdir --help